Japanese maples, especially acer palmatum japanese maple bonsai trees, are among the most picturesque and sought-after species for bonsai cultivation. Their stunning foliage, ranging from deep greens to fiery reds, and the intricate, delicate structure of their branches make them a focal point of any bonsai collection. Growing a Japanese maple bonsai indoors combines traditional bonsai art with modern cultivation technology. This guide will take you through the journey of nurturing these exquisite trees into a living masterpiece.
To embark seamlessly on your bonsai art journey, it's essential to know:
Table of Contents
- Selecting the Perfect Japanese Maple for Your Bonsai Project
- Optimizing Bonsai Health with the Ideal Potting and Soil Mix
- Enhancing Indoor Bonsai Growth with Artificial Light
- Mastering Watering and Fertilization for Your Japanese Maple Bonsai
- Pruning and Shaping Your Japanese Maple Tree Bonsai
- Enhancing Bonsai Vitality through Strategic Repotting and Root Care
- Conclusion
Selecting the Perfect Japanese Maple for Your Bonsai Project

Embarking on the bonsai journey opens up a world where the beauty of nature is condensed into miniature landscapes. The choice of tree is the first and perhaps most pivotal step in this journey, with the Japanese maple(especially acer palmatum) standing out as a prime candidate for bonsai enthusiasts. This section delves into the nuances of choosing the right Japanese maple for your indoor bonsai project, emphasizing the importance of cultivar selection, the appeal of dwarf varieties, and the journey from young trees or cuttings to mature bonsai specimens.
Understanding Japanese Maple Cultivars
The genus Acer palmatum encompasses a diverse range of cultivars, each with its unique characteristics that can influence your bonsai's appearance and growth habit. The choice of cultivar is not just about aesthetics but also about compatibility with the indoor bonsai environment. Dwarf Japanese maple varieties, such as 'Sango Kaku' (renowned for its coral-red bark) and 'Sharp's Pygmy' (a compact variety with dense foliage), are celebrated for their slow growth rates and smaller stature. These traits make them particularly well-suited for the confines of a bonsai pot and the limited space of indoor cultivation.
The Significance of Growth Rate and Size
The growth rate and ultimate size of your Japanese maple are critical factors in its suitability for bonsai cultivation. Slow-growing cultivars are preferred because they allow for more controlled shaping and reduce the need for frequent repotting. A manageable size is equally important, as it ensures that your bonsai remains proportionate and harmonious within its container. Dwarf varieties naturally lend themselves to this, offering a miniature version of the majestic outdoor trees while retaining all the desirable characteristics of the species.
From Raw Material to Bonsai Masterpiece
The transformation of a young tree or cutting into a bonsai masterpiece is a journey of creativity and patience. Whether you start with a sapling or a more mature specimen, the early stages of bonsai development involve nurturing the raw material into a form that embodies the essence of the tree in nature. The informal upright style, one of the most popular and natural styles for Japanese maples, highlights the graceful, flowing lines of the tree's structure. This style is particularly forgiving for beginners, allowing the tree's natural inclinations to guide the shaping process while still affording the artist considerable control over the final appearance.
Choosing Your Bonsai Tree
When selecting your Japanese maple, consider not only the cultivar's visual appeal but also its health and vigor. Look for a tree with a strong, well-defined trunk and an evenly distributed branch structure. The roots should be healthy and not pot-bound, indicating that the tree is ready for transplantation and further training. Remember, the best bonsai specimens start with a solid foundation, so choose a tree that speaks to your aesthetic sensibilities and meets the practical requirements of bonsai cultivation.
In conclusion, selecting the right Japanese maple cultivar for your bonsai project is a critical step that sets the stage for the entire cultivation process. By choosing a variety that is well-suited to indoor growth and aligns with your desired aesthetic, you lay the groundwork for a rewarding bonsai journey. As you nurture your tree from a young sapling or cutting into a bonsai, you'll develop a deeper connection with your plant, understanding its unique needs and shaping it into a living work of art that reflects both its natural beauty and your personal vision.
Optimizing Bonsai Health with the Ideal Potting and Soil Mix
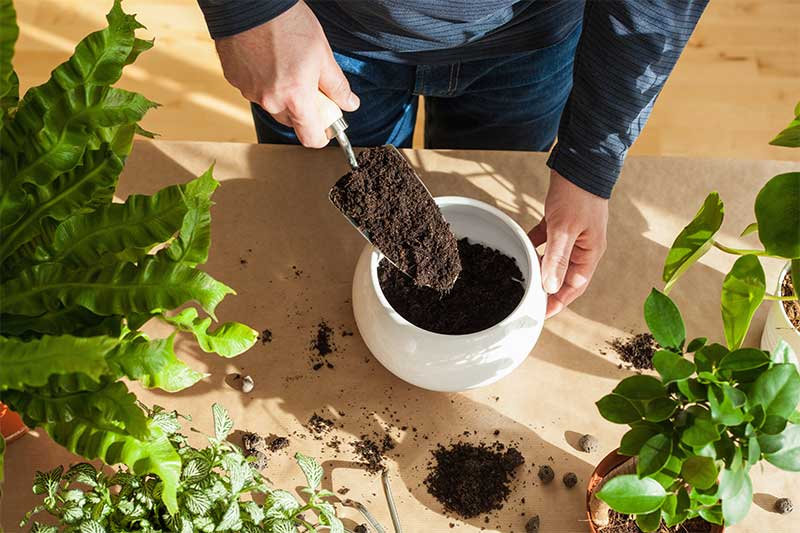

The foundation of a thriving bonsai lies in its potting and soil composition. This aspect of bonsai care goes beyond the superficial beauty of the pot and delves into the critical factors that influence the overall health and growth of your Japanese maple bonsai. The selection of the appropriate bonsai pot, coupled with a carefully crafted soil mix, is pivotal in creating an environment that supports the delicate balance required for the tree’s prosperity. Let’s explore the intricacies of choosing the right pot and formulating the optimal soil mix for your Japanese maple bonsai.
Selecting the Right Bonsai Pot
The choice of bonsai pot is integral to the health and aesthetic appeal of your bonsai. The ideal pot not only complements the visual aspects of your tree but also serves essential functional purposes. Key considerations include:
- Size and Depth: The pot should be proportional to the size of your tree, with enough depth to accommodate the root system comfortably. A pot that is too small may restrict root growth, while one that is too large can lead to water retention and potential root rot.
- Drainage: Proper drainage is critical. Look for pots with adequate drainage holes to ensure excess water can escape, preventing the roots from sitting in water and reducing the risk of root rot.
- Material: Bonsai pots are made from various materials, including ceramic, clay, and plastic. Ceramic and clay pots offer better breathability, which can be beneficial for root health.
Crafting the Perfect Soil Mix
The ideal soil mix for a Japanese maple bonsai must strike a balance between retaining moisture and allowing excess water to drain away. A mixture of akadama, pumice, and lava rock is often recommended for its ability to meet these requirements. Each component plays a vital role:
- Akadama: A naturally occurring, clay-like soil that provides excellent water retention while still allowing air to reach the roots. Over time, akadama breaks down, encouraging fine root growth.
- Pumice: This volcanic rock aids in aeration and drainage, helping to keep the soil loose and preventing compaction. It also retains a small amount of moisture, contributing to the overall hydration of the bonsai.
- Lava Rock: Adds structure to the soil mix, improving drainage and aeration. Its porous nature helps to balance moisture levels within the soil.
The ratio of these components can be adjusted based on your specific environment and the needs of your Japanese maple. A common starting point is a mix of 1/3 akadama, 1/3 pumice, and 1/3 lava rock. This combination can be tailored to increase or decrease drainage and moisture retention as needed.
Monitoring and Adjustments
The environmental conditions where you keep your bonsai will influence the soil’s performance. Humidity, temperature, and the amount of light your bonsai receives can all impact how quickly the soil dries out. Regular monitoring of the soil moisture is essential, and adjustments to your watering schedule or soil mix may be necessary to maintain the optimal conditions for your bonsai’s health.
The careful selection of a bonsai pot and the crafting of a suitable soil mix are crucial steps in ensuring the vitality of your Japanese maple bonsai. By understanding the functional requirements and adjusting the soil components to cater to the specific needs of your bonsai, you create a nurturing environment that supports robust growth and the flourishing beauty of your miniature tree. This attention to detail in potting and soil composition lays the groundwork for a successful bonsai cultivation journey, highlighting the harmonious blend of art and science that is central to the bonsai tradition.
Enhancing Indoor Bonsai Growth with Artificial Light
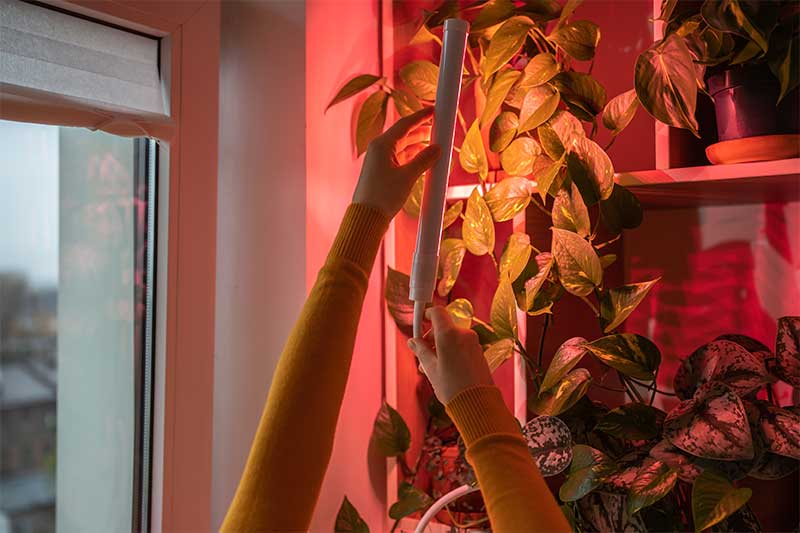

Artifical lights are transforming the practice of indoor bonsai cultivation by offering an advanced, controlled lighting environment that closely simulates the spectrum of natural sunlight. These lights are particularly suitable for nurturing Japanese maples, a species that prefers the gentle embrace of indirect sunlight over the potentially harsh rays of direct sun exposure. Understanding the features and proper use of these lights can significantly enhance the growth and health of your bonsai, allowing for a more efficient and targeted approach to light management.
Tailoring Light to Mimic Natural Conditions
The artifical lights are engineered to provide a broad spectrum of light, covering the essential wavelengths needed for healthy plant growth. This spectrum includes both the blue and red parts of the light spectrum, which are crucial for photosynthesis and stimulating root development. The ability to mimic the sunlight's natural variability supports the development of strong, healthy Japanese maples by promoting vigorous yet controlled growth.
Adjustable Intensity and Duration
One of the standout features of the grow lights is their adjustable intensity settings. This allows bonsai growers to tailor the light to the specific needs of their Japanese maple, ensuring that the tree receives the optimal light intensity without the risk of leaf scorch or excessive heat exposure. During the growing season, setting the lights to operate for 12-14 hours a day replicates the long days of summer, providing your bonsai with the cues it needs to focus energy on growth.
The flexibility to adjust the duration of light exposure is particularly beneficial during the different stages of your bonsai's life cycle. For example, during the dormant winter months, reducing the light duration can help mimic the natural seasonal changes, giving your tree a much-needed rest.
Positioning for Perfect Coverage
The design of the lights facilitates easy positioning and adjustment, ensuring that your bonsai receives uniform light coverage. Proper positioning is key to achieving the best growth results. The lights should be placed above the bonsai, ensuring that the light spreads evenly across the entire canopy. This setup prevents the development of uneven growth patterns and ensures that all parts of the tree receive the light they need to photosynthesize effectively.
For best results, the distance between the LED lights and the bonsai should be adjusted according to the tree's growth stage and the light's intensity. Younger, more delicate trees may benefit from being placed a bit further away from the light source to prevent any potential light stress.
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
Another significant advantage of using LED grow lights for bonsai cultivation is their energy efficiency and long lifespan. Compared to traditional grow lights, LEDs consume less power and generate less heat, making them an eco-friendly and cost-effective choice for indoor gardening. The reduced heat output also means that bonsais can be placed closer to the light source without the risk of heat damage, allowing for more compact and efficient grow setups.
Incorporating LED grow lights into your Japanese maple bonsai cultivation practice offers a sophisticated and effective way to simulate the ideal growing conditions indoors. By providing a spectrum of light that mimics natural sunlight, along with adjustable intensity and duration, these lights empower bonsai enthusiasts to optimize the growth and health of their trees. The careful positioning of these LED lights, combined with their energy efficiency and longevity, makes them an invaluable tool for any bonsai grower seeking to achieve the perfect balance of art and science in their cultivation efforts.
Mastering Watering and Fertilization for Your Japanese Maple Bonsai
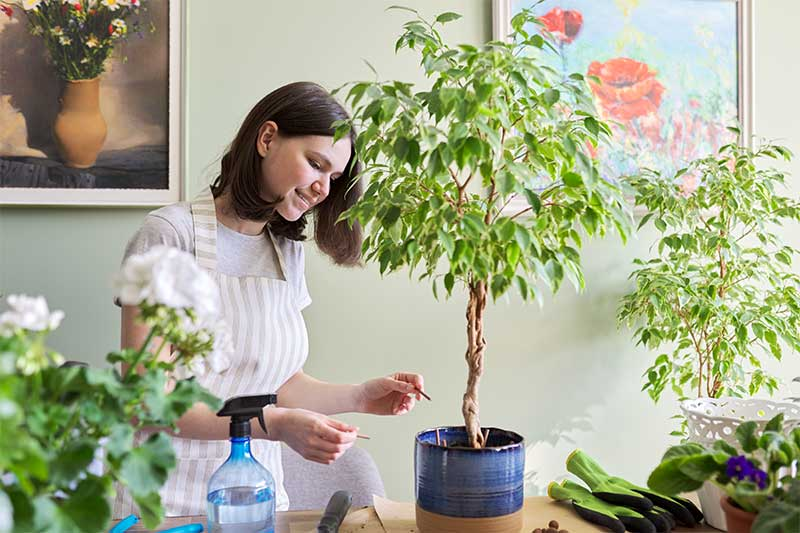

The thriving growth and vibrant health of a Japanese maple bonsai are significantly influenced by proper watering and fertilization practices. These elements of bonsai care are more than routine maintenance; they're an art that balances the tree's immediate needs with its long-term vitality. Understanding the nuances of watering and the strategic application of fertilizers can elevate the health and beauty of your bonsai to new heights.
Precision Watering Techniques
Watering your Japanese maple bonsai requires attention to detail and an understanding of the tree's unique needs. The goal is to maintain soil moisture at a level that supports healthy growth without causing stress from either excess water or drought. This balance is crucial, as Japanese maples are particularly sensitive to water conditions.
- Monitoring Soil Moisture: Before watering, check the soil moisture by touching the soil. If the top layer feels dry, it's time to water; if it still feels moist, wait a day or two and check again. This simple test helps prevent over-watering, which can lead to root rot, a condition that is often fatal for bonsais.
- Watering Technique: When watering, use a fine nozzle to gently soak the soil, ensuring water penetrates the entire root system. Continue until water begins to drain from the bottom of the pot. This method ensures that the roots receive adequate hydration without disturbing the soil structure.
- Adjusting to Seasons: The frequency of watering will vary with the seasons. During the growing season (spring and summer), your bonsai may require more frequent watering, sometimes daily in hot, dry conditions. In contrast, during the dormant winter months, water requirements decrease, and so should your watering frequency.
Fertilization for Optimal Growth
Fertilization is another critical aspect of bonsai care, providing essential nutrients that support the tree's growth, leaf production, and overall health. However, the key is to fertilize judiciously, as over-fertilization can harm your bonsai.
- Choosing the Right Fertilizer: Organic fertilizers are often recommended for Japanese maple bonsais because they release nutrients slowly, reducing the risk of nutrient overload. A balanced liquid fertilizer (with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) is also effective, especially during the active growing season.
- Application Schedule: Apply fertilizer every few weeks during the growing season, starting in late spring and continuing through summer. The exact frequency and amount depend on the fertilizer's strength and the specific needs of your bonsai. Always follow the product's instructions to avoid overfeeding.
- Winter Care: As your Japanese maple enters dormancy in the winter, its nutrient requirements decrease significantly. During this time, reduce fertilization to prevent unnecessary stress on the tree. Some growers stop fertilizing altogether in the winter, resuming only as new growth appears in spring.
Watering and fertilization are foundational elements of bonsai care that demand both precision and intuition. By maintaining the soil at the correct moisture level and providing nutrients without overfeeding, you create an environment where your Japanese maple bonsai can flourish. Remember, each tree is unique, and its needs can change with the environment, the season, and its stage of growth. Regular observation and adjustment of your watering and fertilization practices will help ensure that your bonsai remains a vibrant and healthy miniature representation of nature's majesty.
Pruning and Shaping Your Japanese Maple Tree Bonsai

Pruning and shaping are at the heart of bonsai artistry, transforming an ordinary tree into a miniature yet majestic reflection of nature. For Japanese maple bonsais, these practices are especially critical due to their intricate branch structures and stunning foliage. Mastering the art of pruning and shaping not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of your bonsai but also promotes its health and longevity. Let's delve into the refined techniques that will elevate your bonsai cultivation.
Strategic Pruning for Health and Aesthetics
Pruning is not merely about maintaining size; it's a deliberate process aimed at sculpting the tree while ensuring its health and vigor. For Japanese maple bonsais, this involves a combination of structural pruning and maintenance pruning.
- Structural Pruning: This type of pruning focuses on the tree's overall architecture and is best performed during the dormant season, usually in late winter or early spring before the sap starts to flow. The goal is to remove any competing leaders, dead or diseased branches, and any growth that detracts from the tree's desired form. Structural pruning is critical in the early years of the bonsai's life to establish its shape.
- Maintenance Pruning: Throughout the growing season, maintenance pruning targets new shoots and thinner branches to refine the tree's shape, encourage the growth of smaller leaves, and maintain shorter internodes. This practice keeps the tree compact and encourages a denser canopy. When pruning, make clean cuts close to the branch or trunk to prevent unsightly stubs that can hinder the tree's natural healing process.
Utilizing Wound Sealant for Protection
After heavy pruning, applying a wound sealant is crucial to protect the exposed areas from fungal infections and pests, as well as to promote faster healing. Choose a sealant specifically designed for bonsai or horticultural use, applying it directly to cuts larger than a quarter-inch in diameter. This not only aids in the tree's recovery but also minimizes the risk of disease entry through the pruning wounds.
Embracing the Informal Upright Style
The informal upright style (Moyogi) is particularly well-suited to Japanese maples, capturing their inherent grace and organic growth patterns. This style is characterized by a trunk that curves naturally, with branches that extend outward to form a balanced, yet asymmetrical shape. Achieving this requires thoughtful pruning to remove any growth that disrupts the tree's fluid lines, as well as selective thinning to allow light into the canopy and promote air circulation.
Leaf Pruning for Finer Foliage
Leaf pruning is a technique used to reduce leaf size and encourage the development of denser foliage. In the summer, selectively remove leaves, especially larger ones, to allow light to reach the interior branches. This stimulates back-budding and the growth of new, smaller leaves, enhancing the tree's miniature appearance. However, leaf pruning should be done sparingly to avoid stressing the tree, focusing on no more than one-third of the foliage at a time.
The Art of Wiring
Wiring is a powerful shaping tool in bonsai, allowing you to direct the growth of branches to create your desired form. Use aluminum or copper wire, choosing a gauge that is strong enough to hold the branch in place but flexible enough to be manipulated without damaging the tree. Wrap the wire around the branch in a gentle spiral, being mindful not to wrap too tightly as this can cut into the growing bark. Monitor the wired branches regularly, removing the wire before it embeds into the bark, typically within a few months.
Pruning and shaping your Japanese maple bonsai is a delicate balance of art and science, requiring patience, precision, and an understanding of the tree's natural tendencies. By employing these advanced techniques, you can guide your bonsai towards its ideal form, creating a living sculpture that embodies the beauty and resilience of nature. Remember, each cut and adjustment is a step in the ongoing dialogue between artist and tree, a partnership that can yield extraordinary results over time.
Enhancing Bonsai Vitality through Strategic Repotting and Root Care
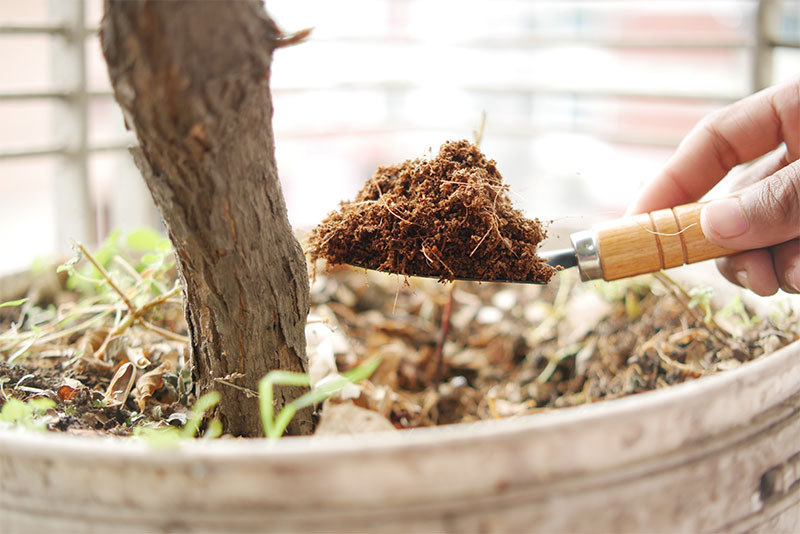

Repotting is a critical component of bonsai care, essential for sustaining a vibrant and healthy tree. This process not only rejuvenates the root system of your Japanese maple bonsai but also ensures the longevity and aesthetic appeal of your miniature tree. Understanding the intricacies of repotting and root care can significantly impact the overall health and development of your bonsai, providing it with the foundation it needs to thrive.
Timing and Frequency of Repotting
The optimal timing for repotting your Japanese maple bonsai is in the early spring, just as the tree begins to emerge from dormancy but before the new growth starts. This timing takes advantage of the tree's natural growth cycle, minimizing stress and allowing for rapid recovery. The general recommendation is to repot your bonsai every one to two years, but this can vary based on the age of the tree, the size of the pot, and the growth rate of the roots. Younger trees, which grow more rapidly, may require more frequent repotting, while older, more mature trees can be repotted less often.
The Repotting Process
Repotting a bonsai involves several key steps, each designed to promote the health and stability of the tree:
- Preparation: Begin by preparing the new pot and soil mix. Ensure the pot has adequate drainage holes and that your soil mix (typically a blend of akadama, pumice, and lava rock for Japanese maples) is ready.
- Unpotting: Gently remove the bonsai from its current pot, taking care not to damage the trunk or branches. This is an opportunity to inspect the root system for any signs of disease or rot.
- Root Pruning: Using sharp, clean tools, carefully prune the root mass. Remove any dead or rotting roots first, then trim back up to one-third of the live roots to encourage new growth. Root pruning helps to stimulate the development of a dense, fibrous root system, which is essential for the efficient uptake of water and nutrients.
- Soil Replacement: After pruning, place the bonsai in its new pot and fill in around it with fresh soil. Work the soil gently around the roots to eliminate air pockets, ensuring that the tree is stable and well-supported.
The Importance of Root Care
Root care goes beyond the act of repotting and involves ongoing attention to the health and structure of the root system. A healthy root system is crucial for the absorption of water and nutrients, which are vital for the tree's growth and development. After repotting, pay close attention to watering, as the newly pruned roots will require careful hydration to recover and grow. Avoid fertilizing immediately after repotting to prevent burning the new roots; wait until new growth appears, indicating that the tree has begun to recover.
Soil Compaction and Nutrient Access
One of the primary reasons for repotting is to prevent soil compaction, which can severely restrict root growth and limit the tree's access to nutrients. Over time, the soil in a bonsai pot becomes compacted from watering and root growth, making it difficult for water and air to penetrate. By replacing the compacted soil with a fresh, loose mix, you ensure that the roots have the oxygen, moisture, and nutrients they need to flourish.
Repotting and root care are essential practices in the art of bonsai cultivation, vital for maintaining the health, beauty, and longevity of your Japanese maple. By following a thoughtful and informed approach to repotting, you provide your bonsai with the foundation it needs to thrive, ensuring that it continues to delight and inspire for years to come.
Conclusion
The journey of growing a Japanese maple bonsai indoors is a blend of art and science, requiring patience, precision, and a bit of creativity. With the support of LED grow lights, this endeavor becomes not only possible but immensely gratifying. As your bonsai matures, it becomes not just a small tree in a pot but a testament to the beauty of nature and the rewarding art form of bonsai cultivation. Whether you're a seasoned bonsai grower or a newcomer eager to embark on this fascinating hobby, the Japanese maple offers a canvas like no other.